Stirring is one of the most common activities where analysis is carried out, and laboratory stirrers are the tools that are used.
The purpose is to mix different substances - solutions, reagents, etc. - thus creating mixtures ready to be analysed.
Stirring with laboratory stirrers can be done in different ways, each to obtain specific results.
Mixing the contents of a beaker or cylinder can be done manually with a glass or PVC rod, which does not spoil even when in contact with corrosive substances. In this case, a stirrer is not necessary, but the manual skill of the operator is sufficient.
There are, however, cases in which the use of an agitator is necessary for various reasons. For example, for the amount of volume to be mixed, for the repetitiveness of the operation to be calculated, for the number of containers to be operated on, and many others.
Depending on the needs, there are devices that can meet individual requirements.
Magnetic stirrers
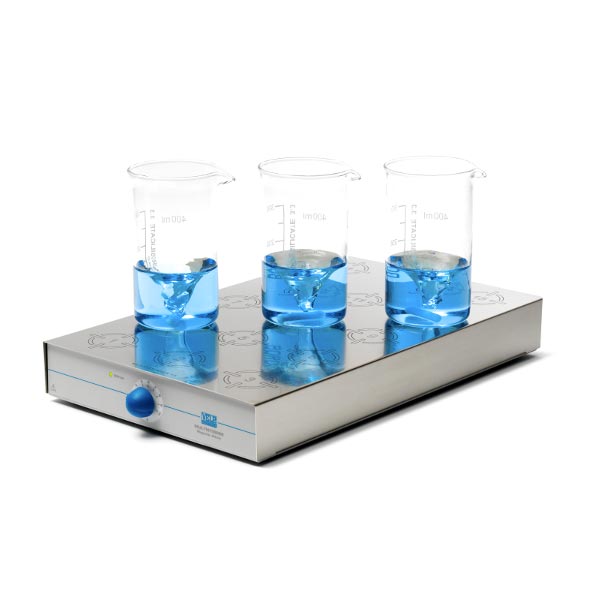
Today's most commonly used laboratory stirrers are magnetic. This type is used to stir without the use of stirring rods or other external mechanical elements, but only with the use of a magnetic stirring rod immersed in the solution.
A magnetic field acts in the device, which moves the stirring rod at the desired speed. Its shape and size determine the effectiveness of stirring depending on the characteristics of the liquid (quantity and quality). Often, good stirring also depends on the container being used.
The agitation speed can be regulated by means of a pulse microprocessor, which enables optimum speed progression.
In our online catalogue there are also models that are maintenance-free because they have no moving mechanical components. The movement is simply generated by coils that induce a rotating magnetic field. Thanks to this, the progression can be controlled easily and the instrument's lifetime is longer than other models.
The different models for sale online have each developed specific features that make them suitable for certain applications. There are models, for example, that maintain a low temperature even after hours of continuous use.
This characteristic makes them suitable for microtitrations and they are used in chemistry and microbiology laboratories.
Other models, due to the special materials and paints with which they are constructed, are suitable for use with corrosive agents to which they are more resistant.
Other magnetic stirrers are used for stirring volumes of up to 25 litres of solution.
Magnetic stirrers are used for stirring volumes of up to 25 litres of solution. The magnetic stirrers are also used for stirring up to 25 litres of solution.
Heating magnetic stirrers
.
For certain processes, magnetic stirrers can also be equipped with heating. This is activated by an electrical heating element placed under the table top. Depending on the quality of the instrument, the temperatures that can be reached vary from a few degrees up to 300°C.
Another element to consider when choosing a stirrer is its size. Agitators on the market have standard dimensions for the most common applications. Some can be built to agitate even large containers.
.
Mechanical Agitators
Mechanical agitation is the traditional form of agitation performed by a tool similar to an immersion blender. This form of agitation is particularly suitable for substances with a higher viscosity than water. The force of the motor determines how thick a liquid can be mixed with that agitator.
Shaking and tilting agitators
.
There is also the need to use laboratory shakers with containers such as test tubes or flasks with calculated movements.
The use of these shakers is particularly used in haematology and diagnostic laboratories. The shaking can be programmed as a tilting type for shaking flasks. These are purposely secured to the work surface with couplings or other fastening systems.
Tilting shakers are designed with a low centre of gravity to prevent containers from slipping on the work surface. Movements are programmable in different options and load capacities.
These agitators can be equipped with a thermostat hood and over-temperature sensors.
The tilting movement can be chosen between two inclinations: a 5° tilt for a gentle movement and a 10° tilt for a more vigorous movement.