Reactors are instruments used in chemistry, and act as a vessel for a chemical reaction. There are numerous types and applications of chemical reactors. The different types of reactors depend on the chemical nature of the substances they must contain, and are designed to ensure the best possible yield with the least expense. In addition, they must take into account the hazardous nature of the reactions and the toxicity of the reagents involved.
Reactors are applied both in laboratory chemistry, generally as glass vessels, and in industrial chemistry. They have dimensions and characteristics tailored to their function. Their material is also varied, they can be made of stainless steel or titanium.
Chemical reactor in the laboratory
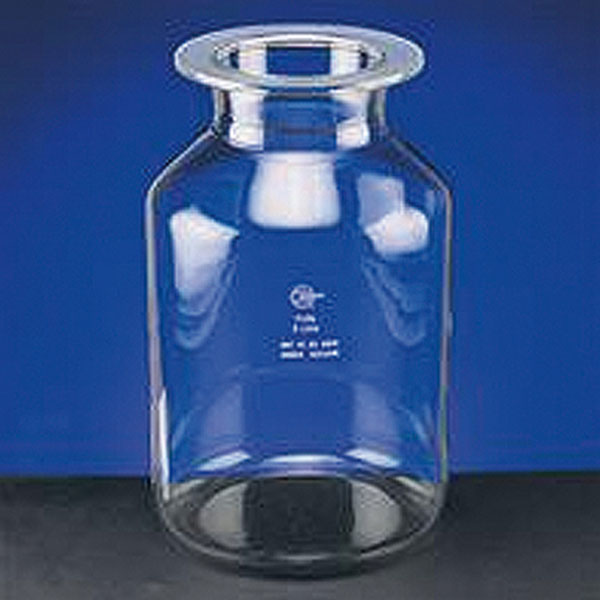
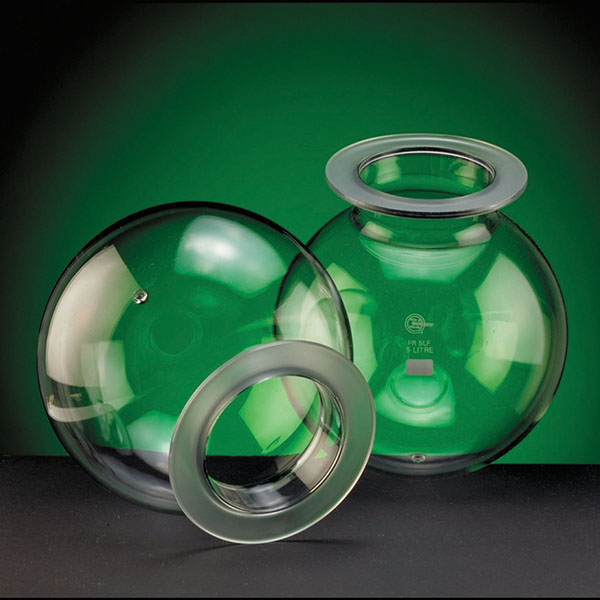
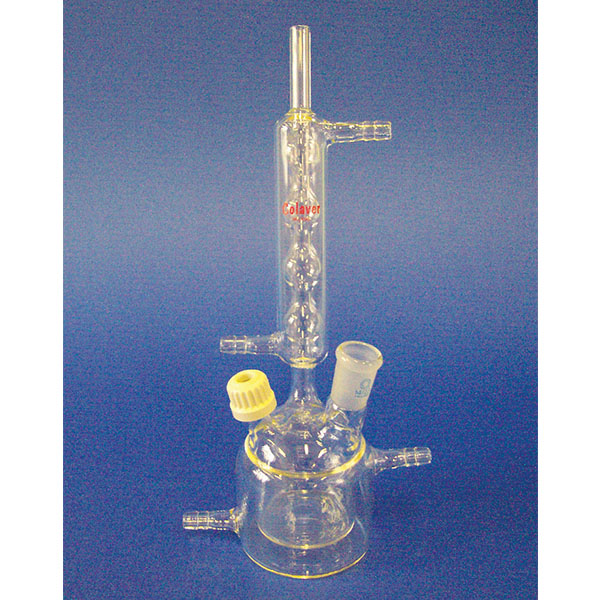
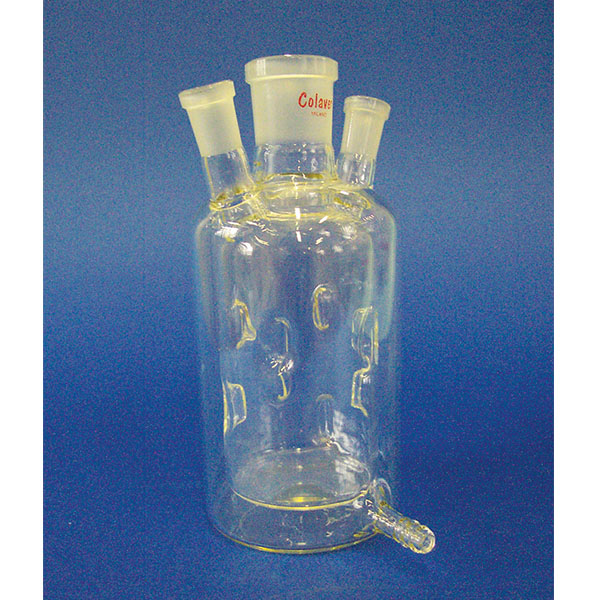
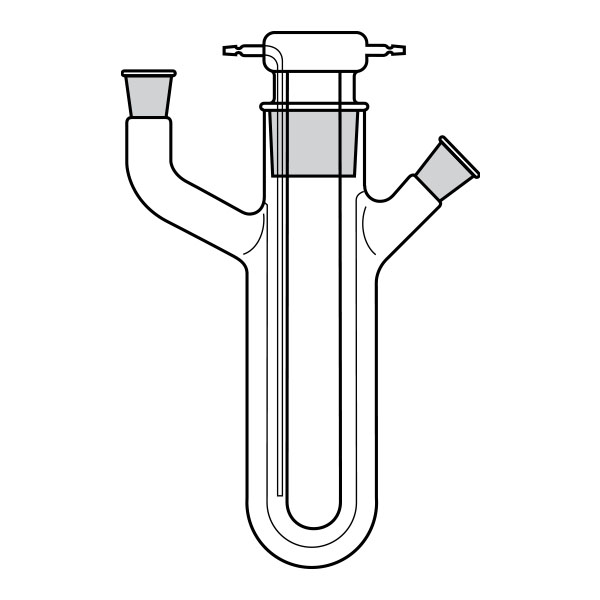
In laboratory chemistry, reactors are generally made of glass. In addition, reactor sizes are clearly smaller than in industrial chemistry. The most commonly used models are cylindrical or spherical in shape. Reactors also differ in their bottom, which can be flat or round.
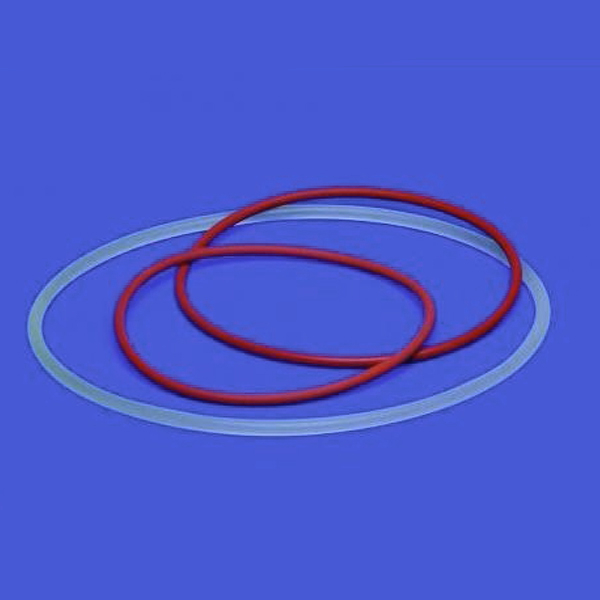
The top section of the reactors, called the flange, is frosted and turned upwards. This is because, once lubricated with silicone gel, it has the task of adhering perfectly to a similar structure under which it is placed.
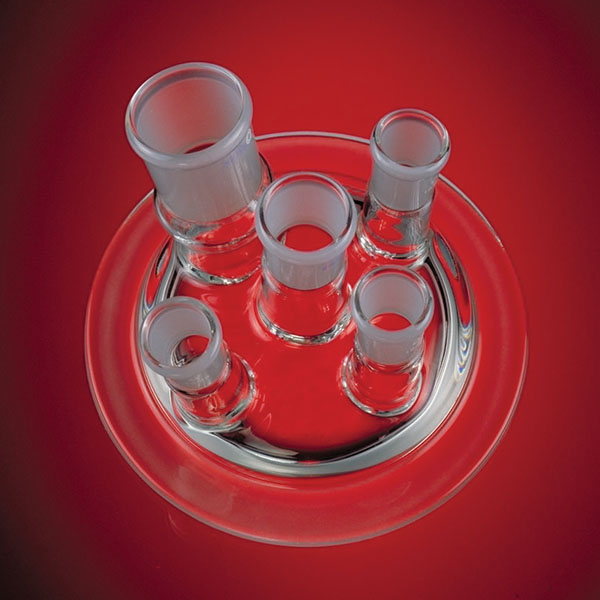
Chambered reactors
.
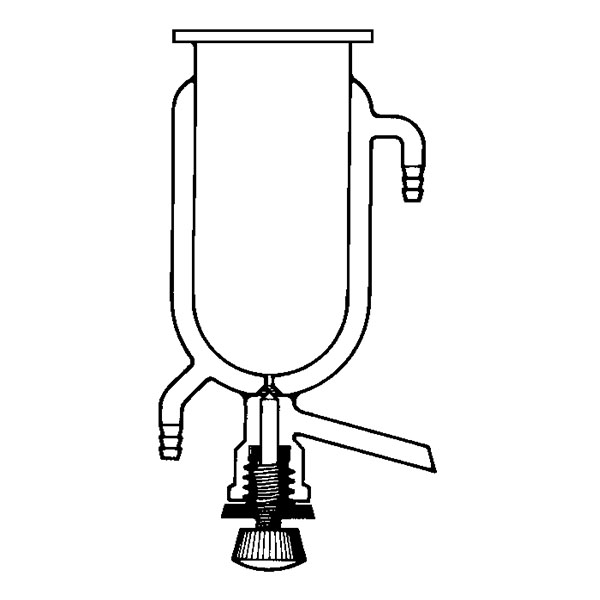
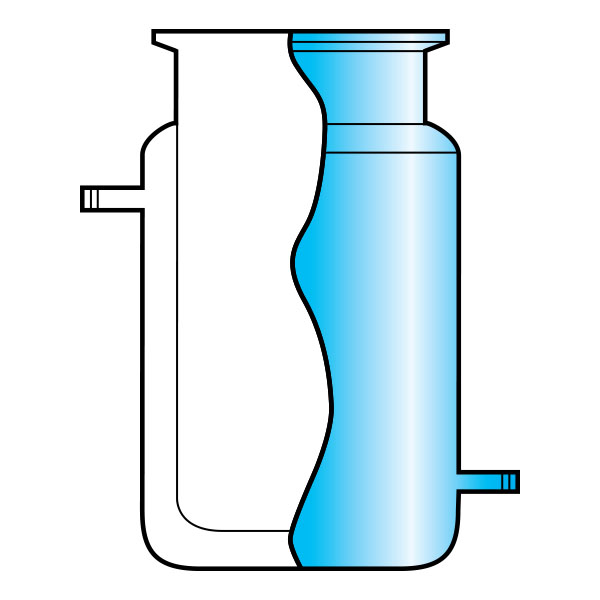
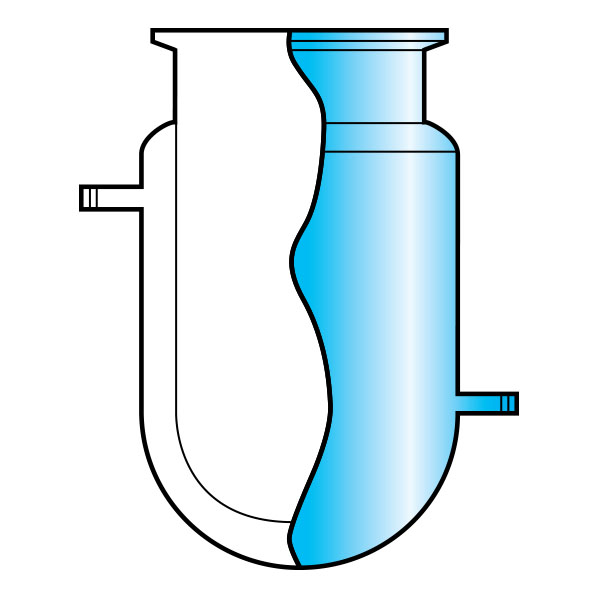
There is a particular type of reactor referred to as a 'jacketed reactor'. In chemical engineering, a jacketed device is defined as a vessel designed to control the temperature of its contents through an additional layer. This is filled with a heating or cooling fluid, depending on its function. In other words, a jacketed reactor has the ability to regulate heat exchange through a 'jacket' that surrounds the container and inside of which is a cooling or heating fluid that comes into direct contact with the reactor's inner walls. The jacket of the reactor is external and separate from its contents, and may cover the reactor completely or only partially.
The "service fluid" is defined as the fluid whose function is to heat or cool the contents of the reactor. The 'process fluid', on the other hand, is the fluid inside the equipment.
Accessories
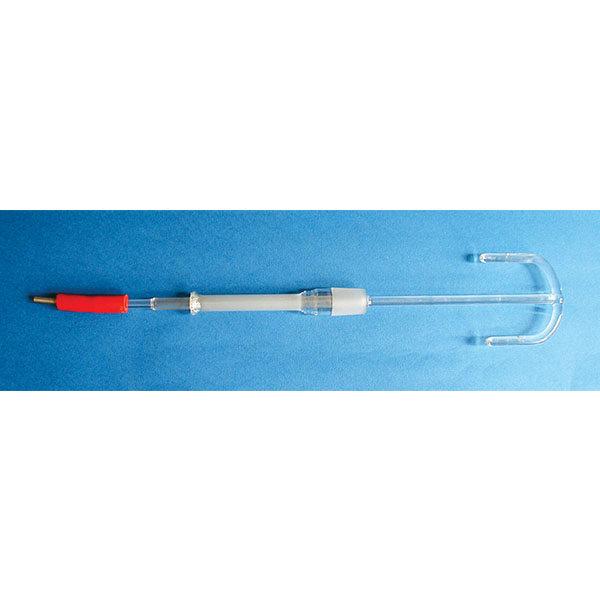
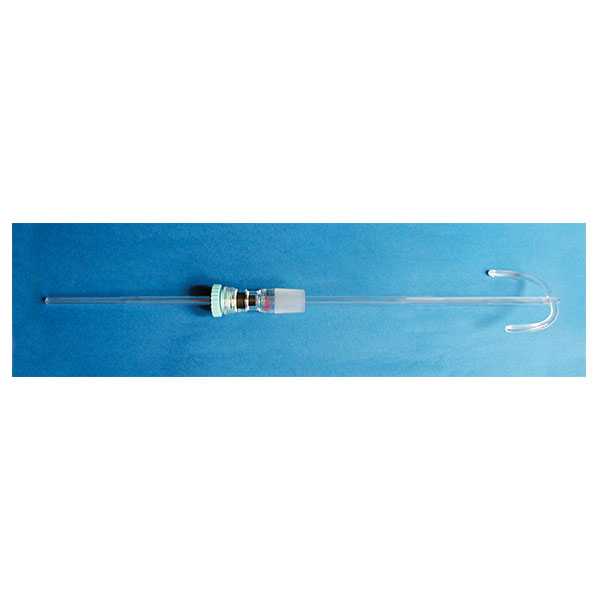
The use of reactors in the laboratory is, in certain cases, aided by an agitator. This is a glass, syringe-type accessory that allows the contents of the stirrer to be mixed and drawn off.
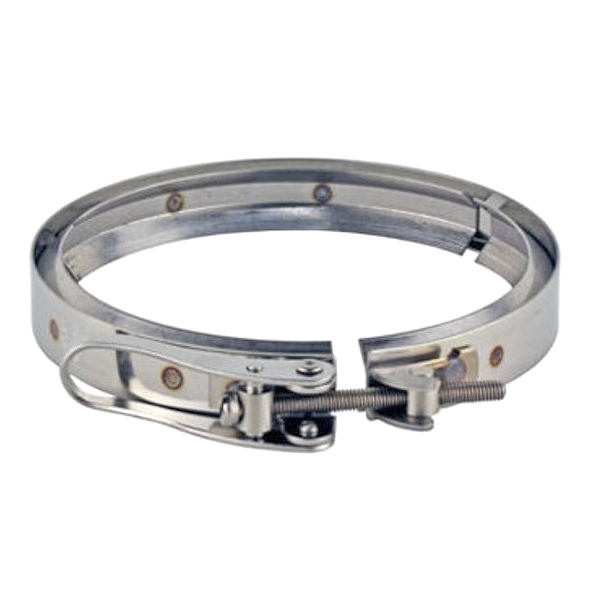
Finally, a further accessory is the metal ferrule. The ferrule is essential to ensure a perfect fit of the ground flange when it is made to coincide with another flange. The ferrule is generally made of steel with silicone seals.
.
To learn more about the chemical reactor click here