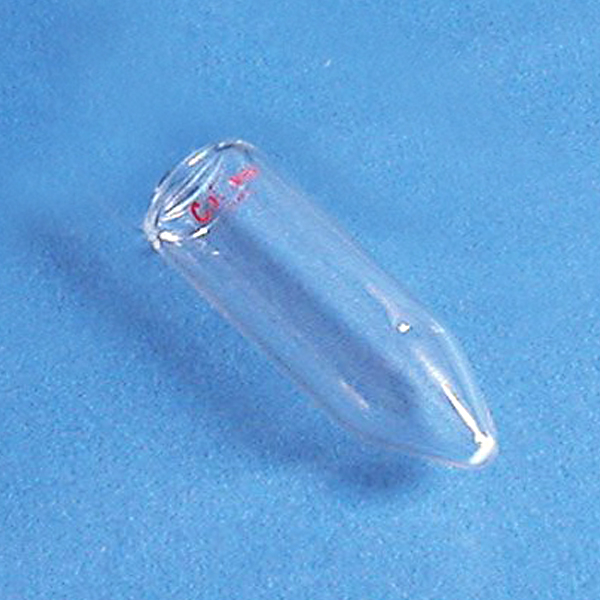
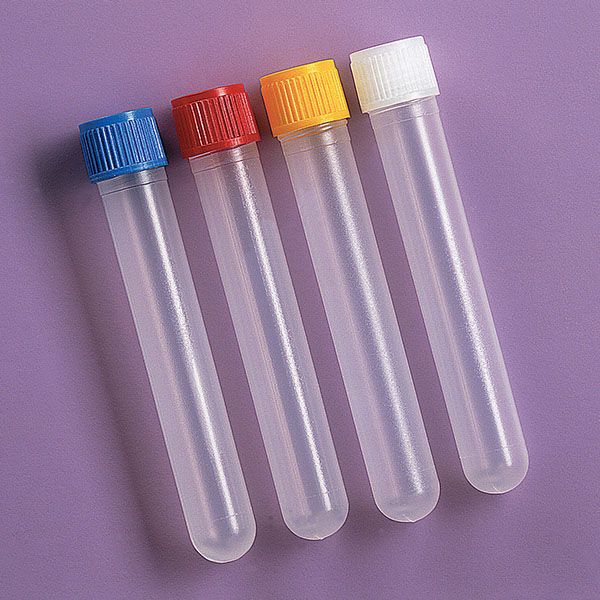
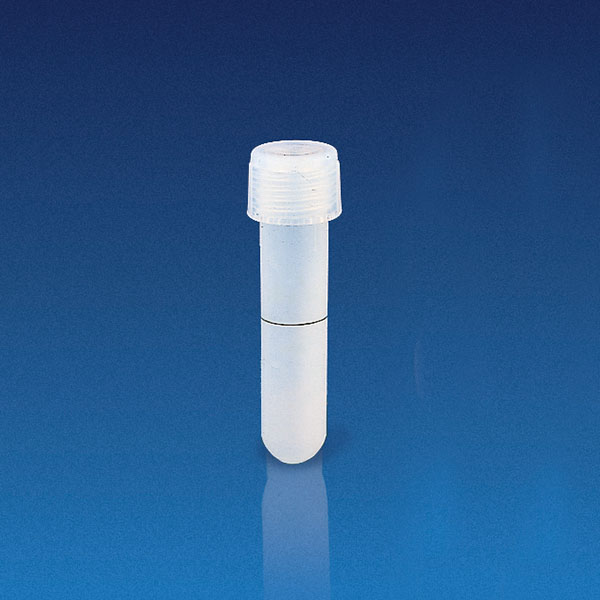
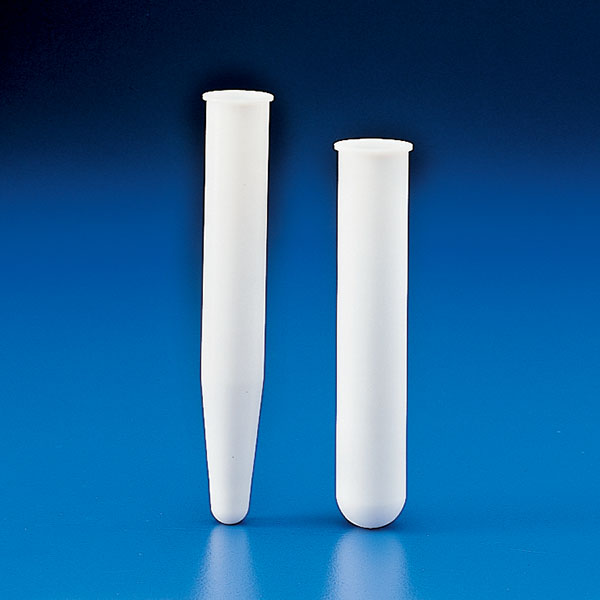
Tubes are cylindrical vessels closed at the bottom that are used in chemistry and experimental laboratories.
This small tube is used to contain the substances to be analysed and has two main types:
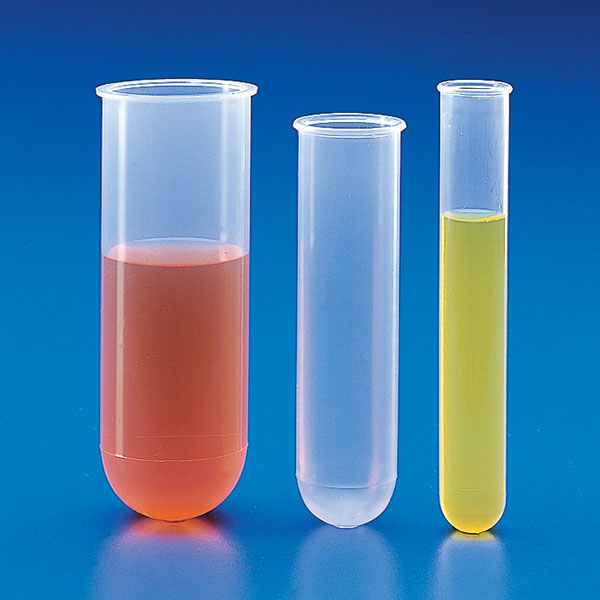
They are used to contain the substances to be analysed.
- with rounded bottom corners are the most common ones;
.
- with conical bottoms are used in centrifuges
.
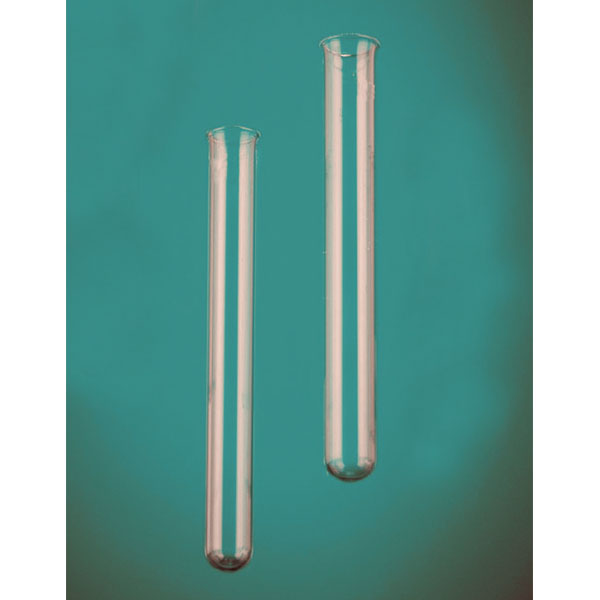
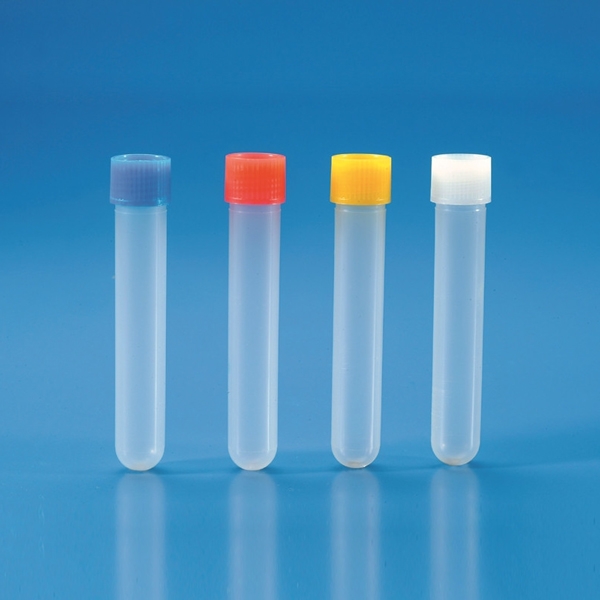
The laboratory test tube
 Standard test tube sizes range from 80-100 mm in length and a diameter of about 8 to 18 mm. But there are test tubes for many uses and of the most varied sizes.
Standard test tube sizes range from 80-100 mm in length and a diameter of about 8 to 18 mm. But there are test tubes for many uses and of the most varied sizes.
.
The Colaver's glassworks can make Pyrex glass test tubes in all sizes and with caps or fittings. Thanks to the use of this material, the test tube can be heated up to high temperatures.
.
This container is used to hold substances that react to mixing and alteration, so it must be able to be heated either with thermostatic baths or directly by flame with Bunsen lamps.
Tubes in different materials
.
They are used in glass when the reaction or the nature of the substances requires a neutral material that does not corrode and is easy to wash.
Tubes also exist in PET plastic material, however, which is very popular, for example, for containing blood.
The unbreakable nature of this material, together with the good sterility to which the test tube is subjected, make it suitable for use in centrifuge tubes. Strong movement could cause the glass to break, so PET tubes are more commonly used for centrifuging.
The most common uses
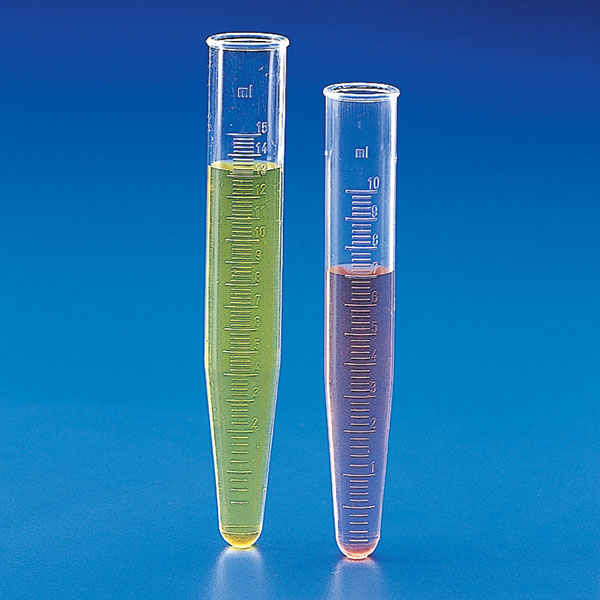
The test tube is widely used to perform analytical tests on substances. After placing the sample of material in the tube, the reagent is added to check whether the expected reaction occurs. For example, a change in the colour of an indicator or the formation of a precipitate is observed.
These terms indicate the reaction that occurs, in the case of indicators, when a compound undergoes visible changes as a result of contact with a substance.
The indicator is usually used to test a substance.
The indicator usually changes colour depending on the chemical environment it is in. This can be acidic, basic, oxidising, rich or poor in a certain ion, etc.
In contrast, the precipitation that can occur is the separation as a solid of a solution that is above its solubility limit. This separation can be caused by a chemical or physical reaction of the solution. For example by heating.
Eppendorf
 Eppendorf test tubes are small conical tubes suitable for centrifugation. They can hold very small amounts of material, from 250 μL to 2 ml.
Eppendorf test tubes are small conical tubes suitable for centrifugation. They can hold very small amounts of material, from 250 μL to 2 ml.
They are used as disposable tubes due to the low cost of the material from which they are made.
Because they are made of polypropylene, they have a wide range of uses due to the material's resistance to different temperatures. It is also resistant to organic solvents such as chloroform.
The name Eppendorf is derived from the company that holds the patent for this product and still markets them today.
Look at the Eppendorf test tubes we have in our catalogue.
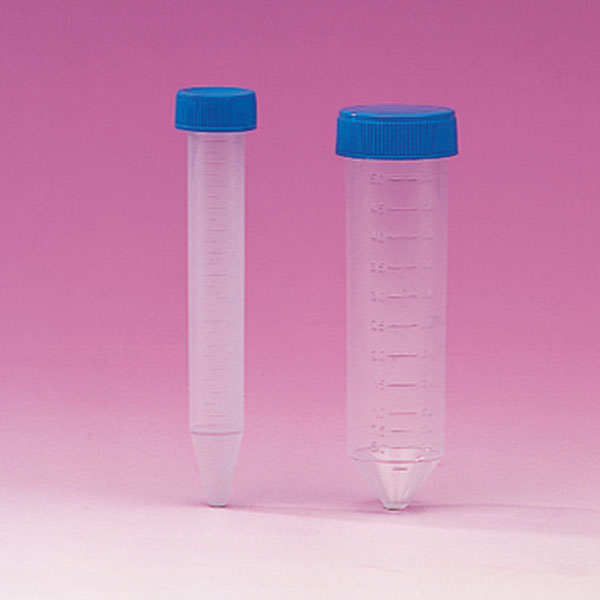
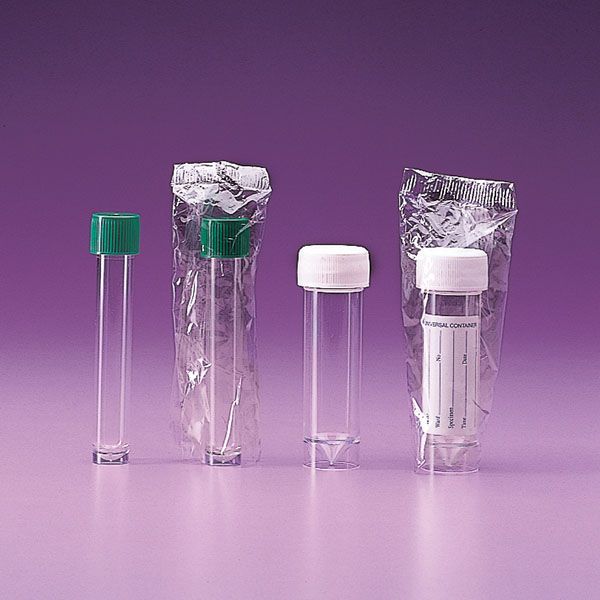
Chemical test tube
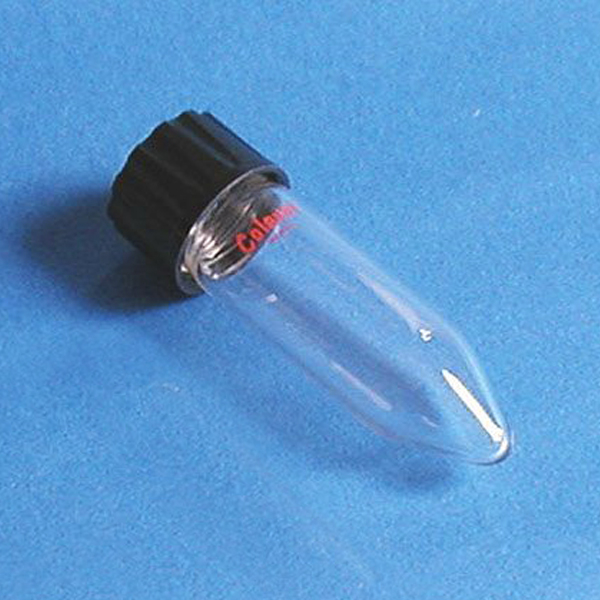
In the laboratory, the svl test tube is the one with a standard thread that allows the cap to be screwed on,
If a gasket is also added, the seal allows any material to be contained.
This is one of the most commonly used test tubes in the laboratory. Check prices and sizes and ask Colaver for a quotation for your laboratory.
Tube Rack
In the laboratory, there is never enough space, but above all, samples must be at hand and kept in maximum order to avoid misclassification.
This is why tube holders are on the market to help keep samples in order and avoid mistakes.
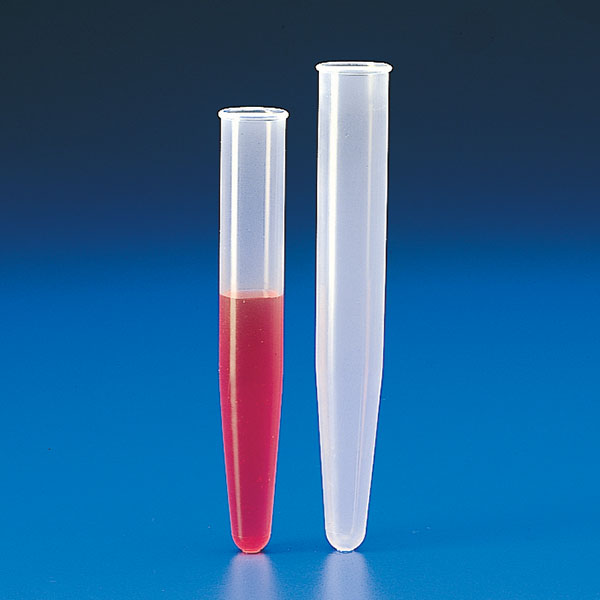
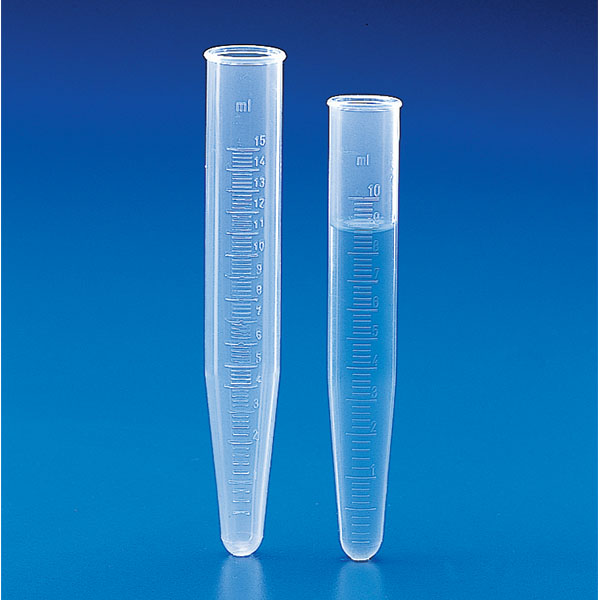
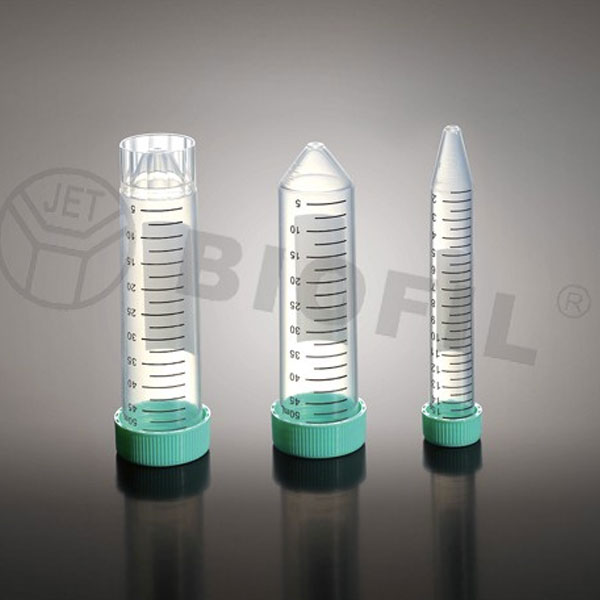
Tube Centrifuge
Special tubes capable of withstanding high speed rotation must be used for centrifuge work.
Depending on the nature of the sample and the work to be done, glass centrifuge tubes or plastic centrifuge tubes.
Centrifuge tubes are characterised by the cone shape of one end.
Centrifuge tubes have a screw cap that ensures the sample is sealed. They are laboratory tubes that can hold organic material, blood and all valuable materials for analysis.
.
Sterile tubes
Sterile test tubes are used in molecular biology applications.
They allow organic material such as DNA and RNA to be stored while minimising the risk of coming into contact with the external environment that would contaminate them. Find out more.



 Standard test tube sizes range from 80-100 mm in length and a diameter of about 8 to 18 mm. But there are test tubes for many uses and of the most varied sizes.
Standard test tube sizes range from 80-100 mm in length and a diameter of about 8 to 18 mm. But there are test tubes for many uses and of the most varied sizes. Eppendorf test tubes are small conical tubes suitable for centrifugation. They can hold very small amounts of material, from 250 μL to 2 ml.
Eppendorf test tubes are small conical tubes suitable for centrifugation. They can hold very small amounts of material, from 250 μL to 2 ml.