The imbute in chemistry is an extremely common tool. They are used for the purpose of pouring liquids or fine-grained substances into narrow-necked containers. They are used daily and are also very common in the home. In the chemistry laboratory, the funnel is used in different materials and shapes.
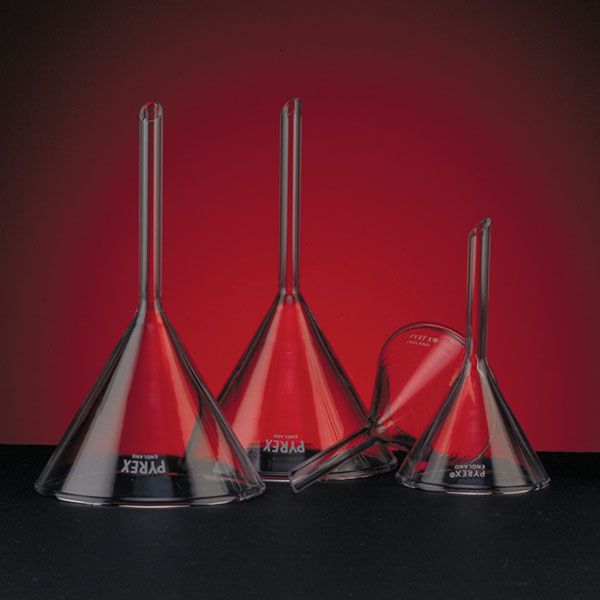
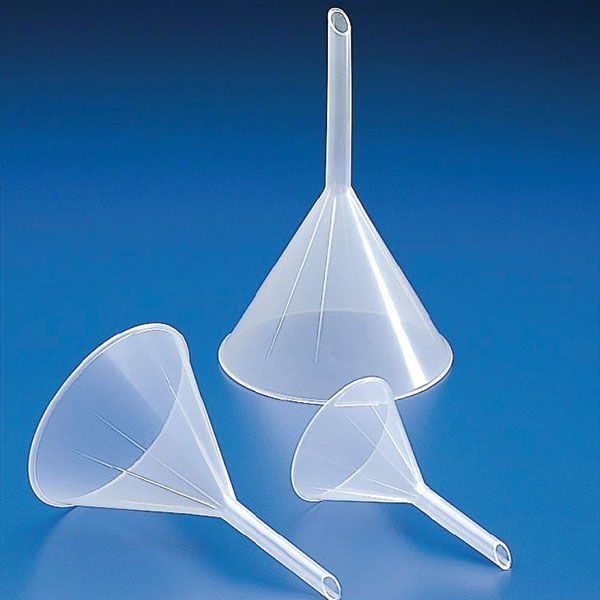
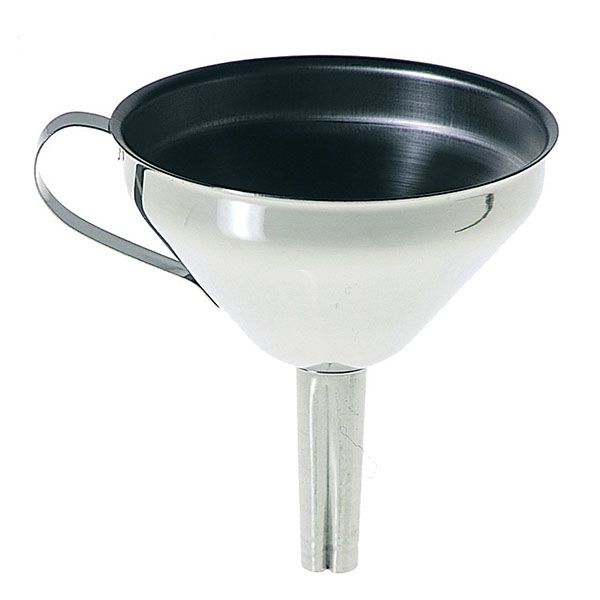
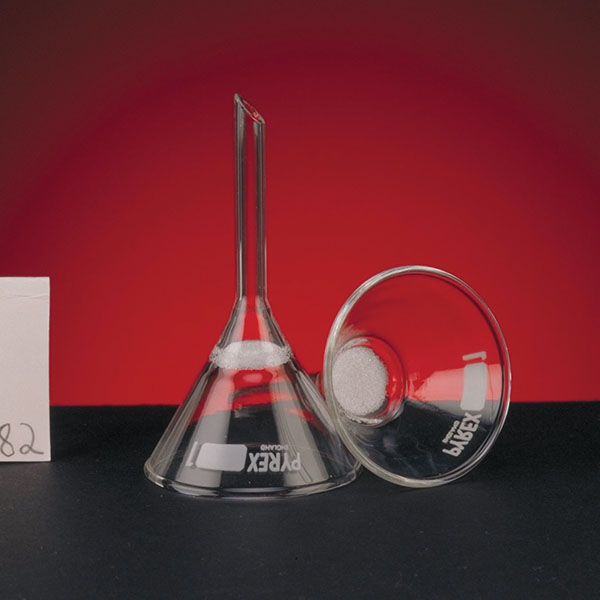
Laboratory Funnel
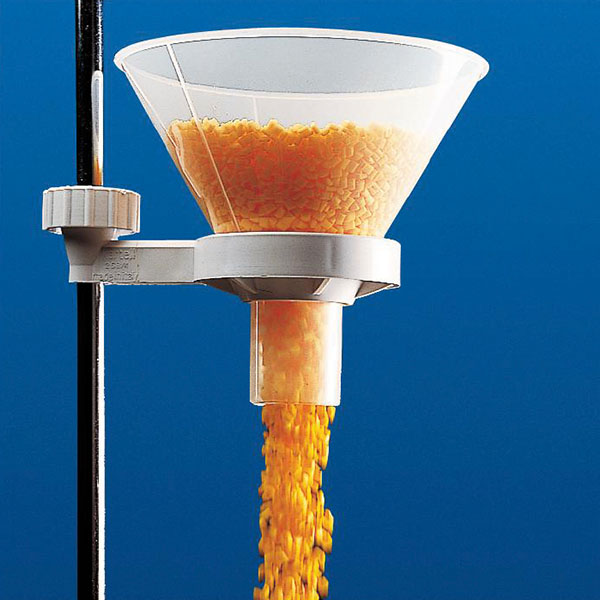
Funnel funnels consist of a cone with an open upper section and a lower section connected to a cylinder, or stem, which allows the liquid to flow out. In standard models, the length of the stem of the funnel is roughly equivalent to that of the cone. However, there are models of the long-stemmed funnel in which it measures approximately twice as long as the cone. A further variation of the standard model can be found in the funnel whose stem is wider. This feature facilitates the flow of material into the funnel, and consequently this model is used for fine-grained substances rather than liquids.

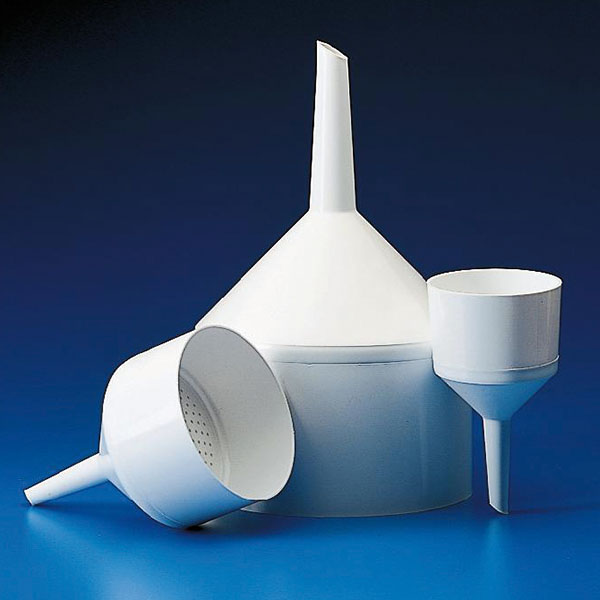
The glass or plastic funnel
The chemical funnel is generally produced in stainless steel, aluminium, glass and plastic. The choice of material depends on what the instrument is used for. It must be borne in mind that the imbute must retain its rigidity when containing the material. This is because it must support the weight of the substance to be transferred. Furthermore, the material must not react with this substance. Consequently, funnels made of steel or glass are used to transfer diesel, while plastic models are used for their use in the kitchen. There is also a funnel model made of paper, usually disposable, which is also used as a cover so as not to soil another funnel.
Funnel and Chemistry
Standard funnels are used in chemistry, but also slightly adapted models to perform useful functions in the laboratory.
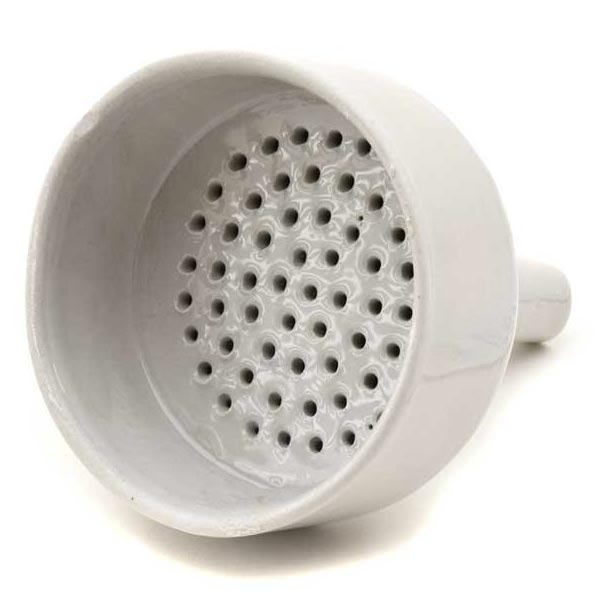
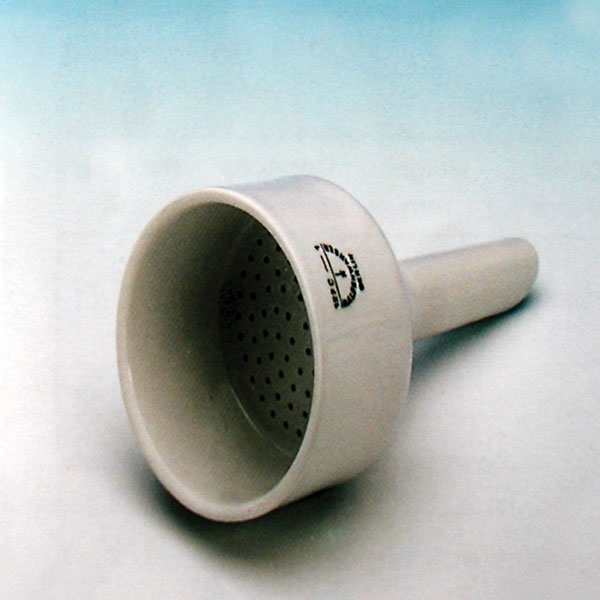
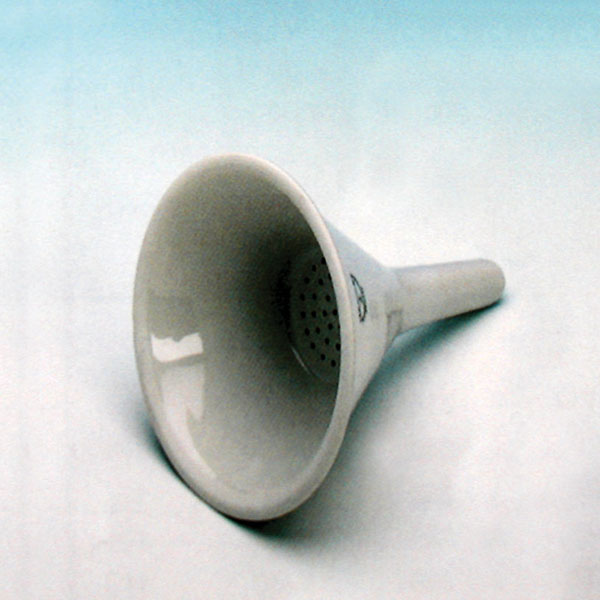
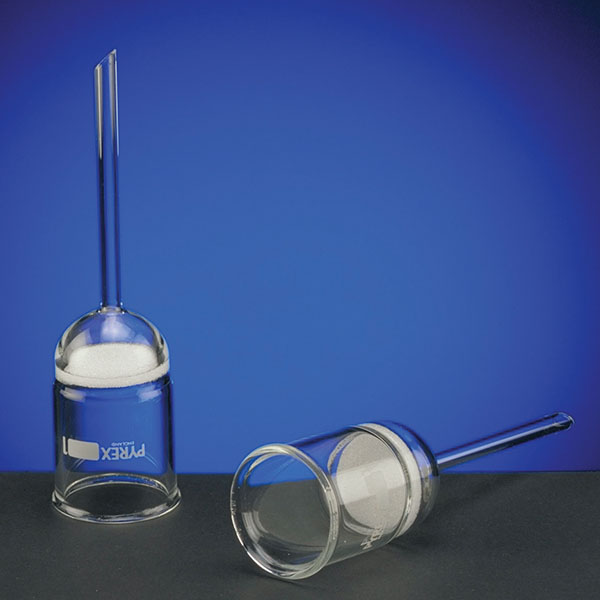
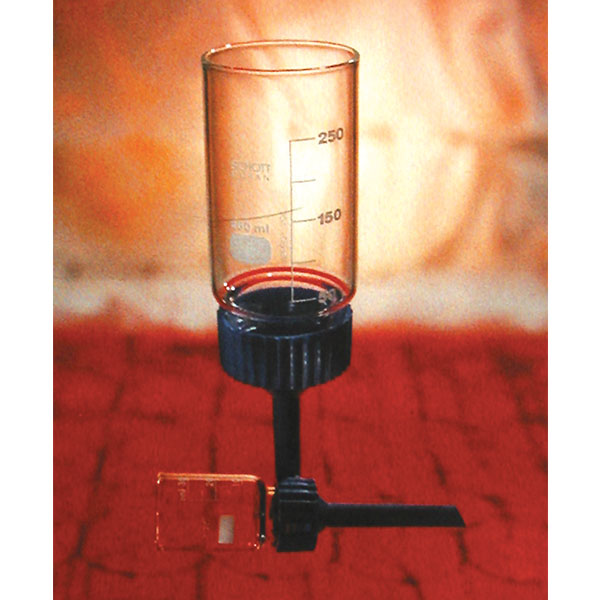
- The filter funnel is characterised by the presence of a porous septum filter between the cone and the stem. It is used to separate solids from liquids by the process of filtration.
- The filter funnel is characterised by the presence of a porous septum between the cone and the stem.
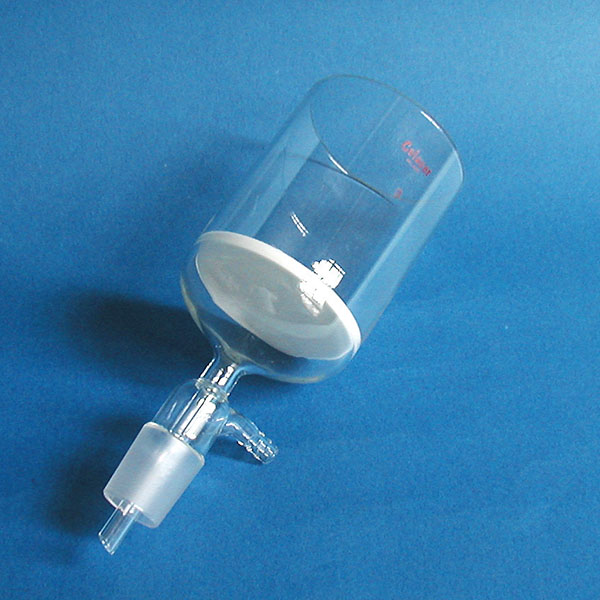
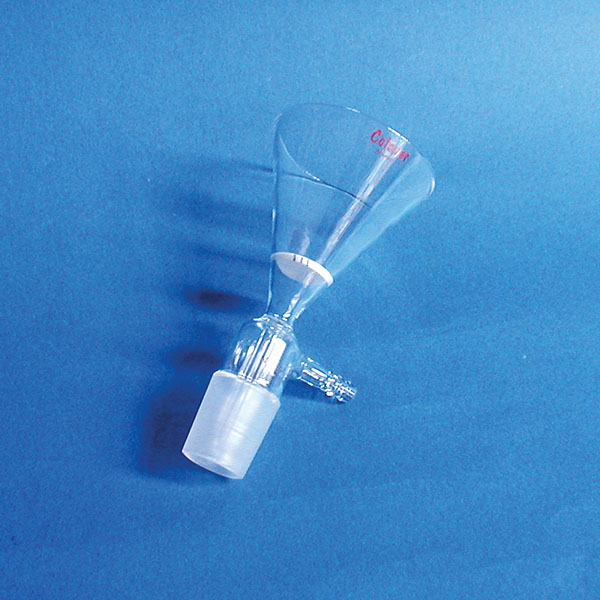
- There is also the separator funnel, used for liquid-liquid extractions, i.e. the separation of liquid mixtures with the aid of a solvent phase. This funnel model has a different shape from the standard model. In fact, it has a hemisphere added on top of the cone, and its stem is usually attached with a Teflon or glass spigot.
The funnel is also used for liquid-liquid extractions.
- Finally, there is also a model referred to as a drip cone. These are used in the laboratory for fluid transfer. They are characterised by the presence of a cap in the lower section, which allows the flow of the funnel's contents to be regulated. Drippers are used to add reagents slowly, e.g. when adding them quickly could cause a reaction or the reaction to be too violent.
.