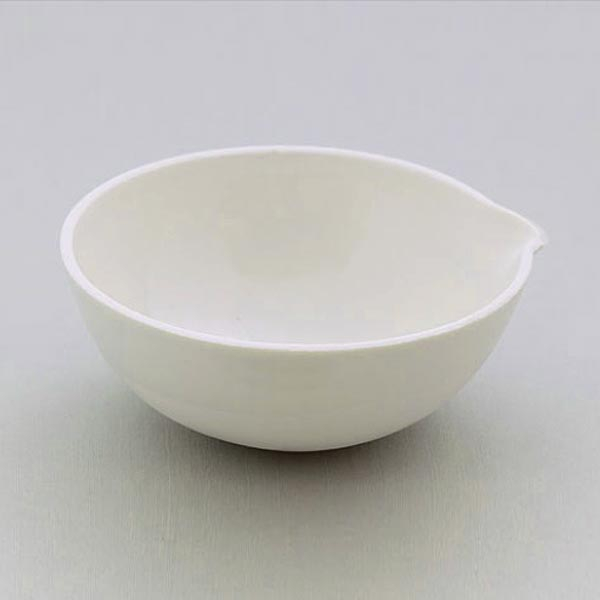
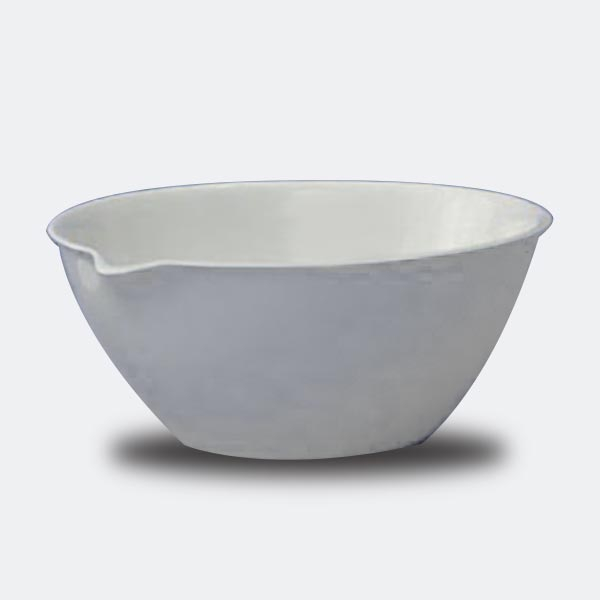
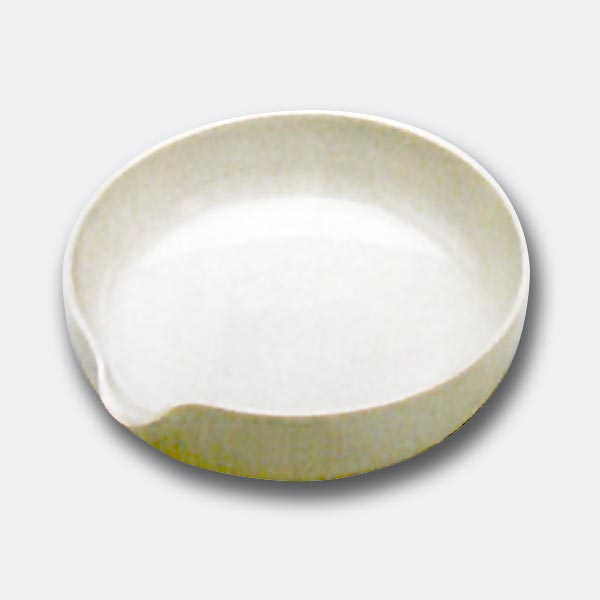
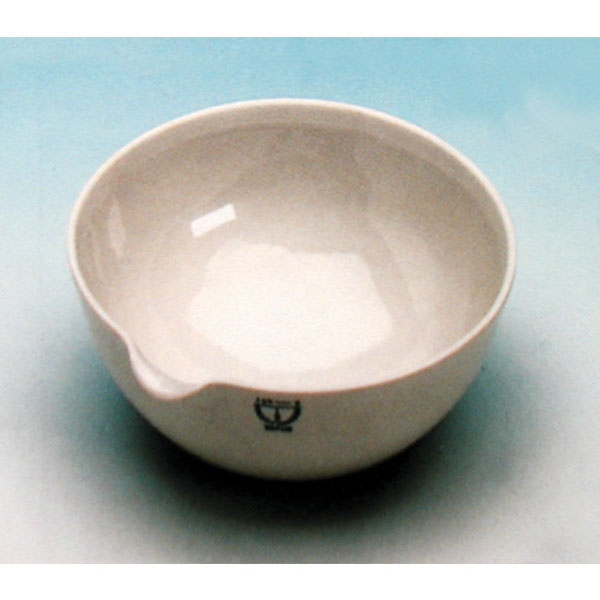
Capsules are equipment used in analytical laboratory chemistry. They usually serve the function of a container or receptacle for substances to be evaporated.
Capsule materials
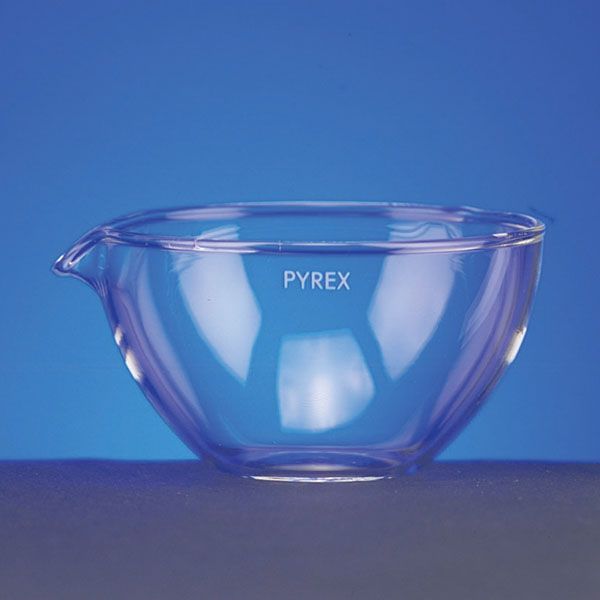
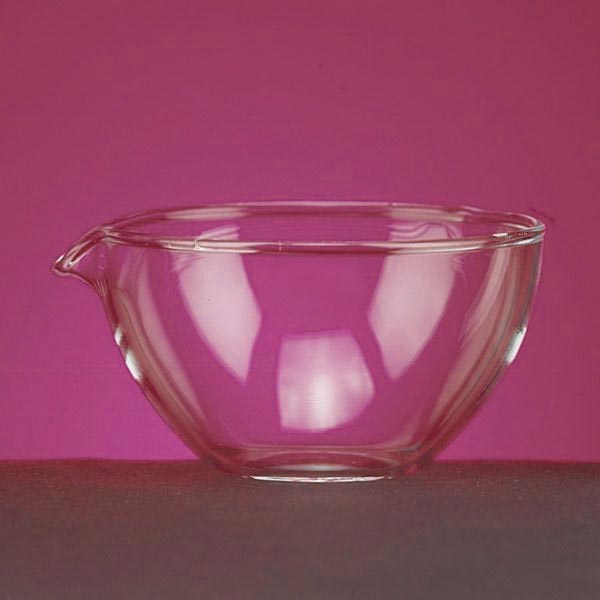
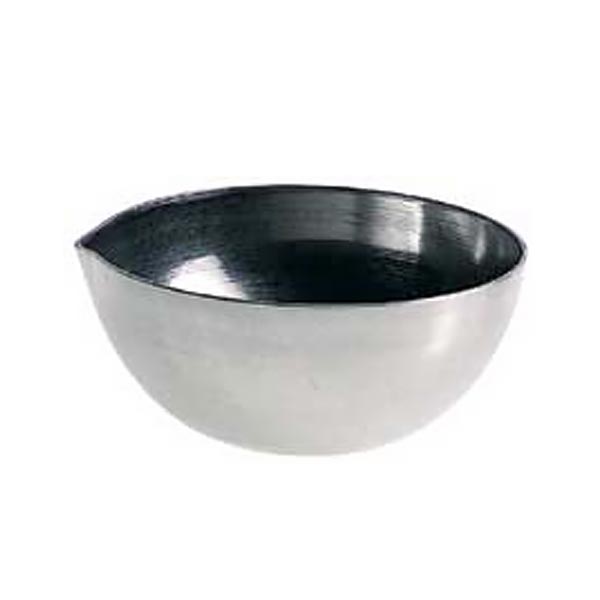
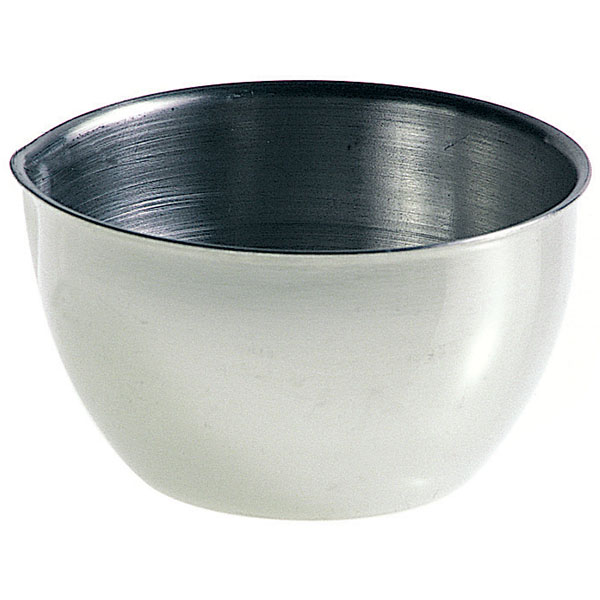
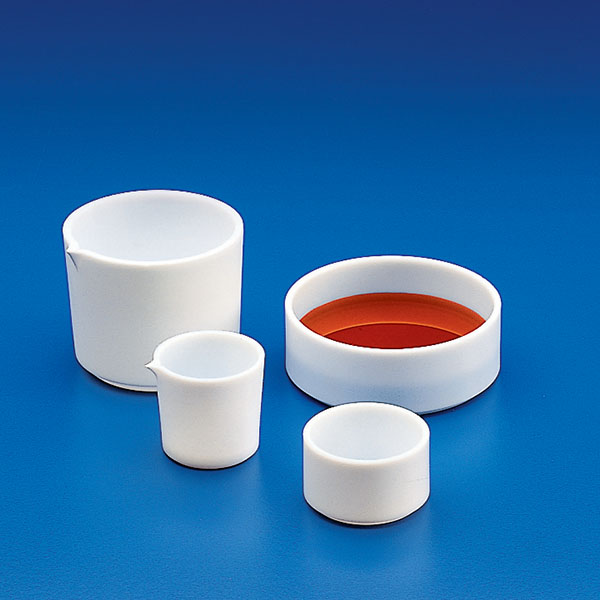
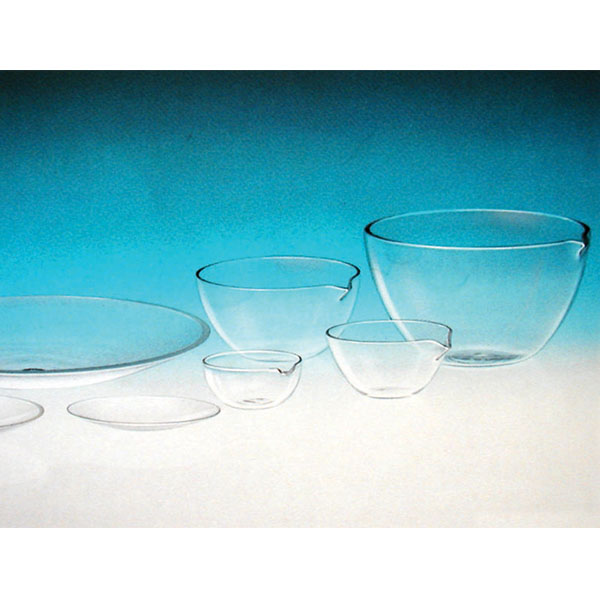
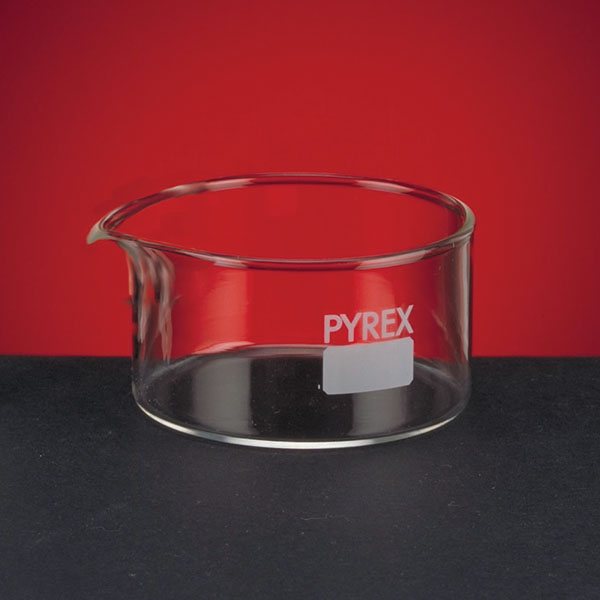
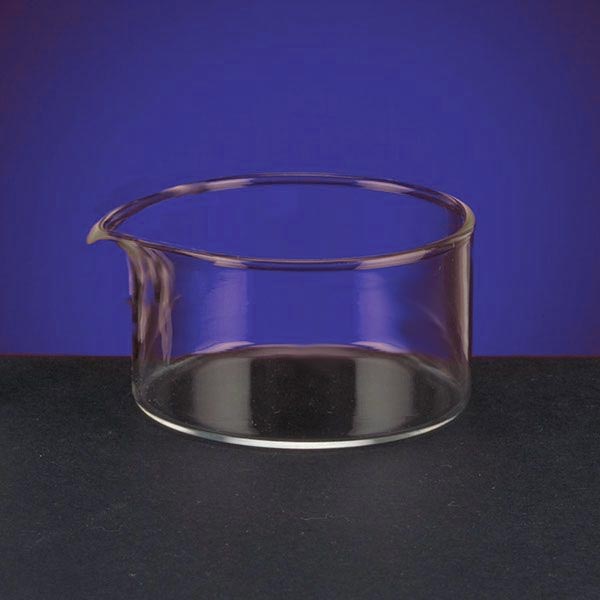
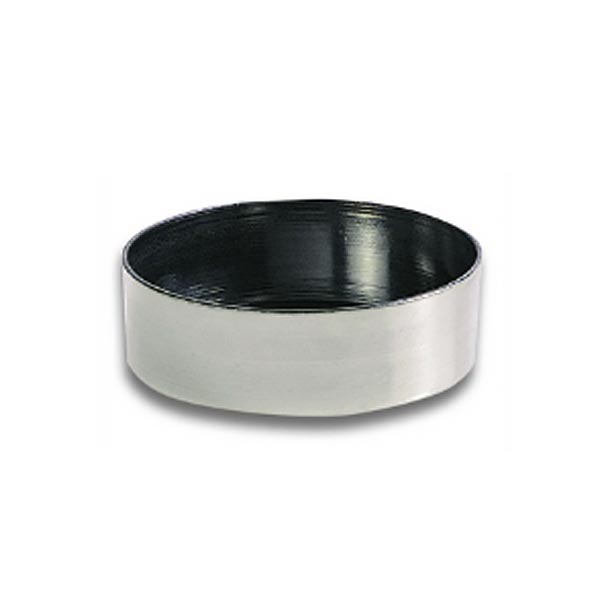
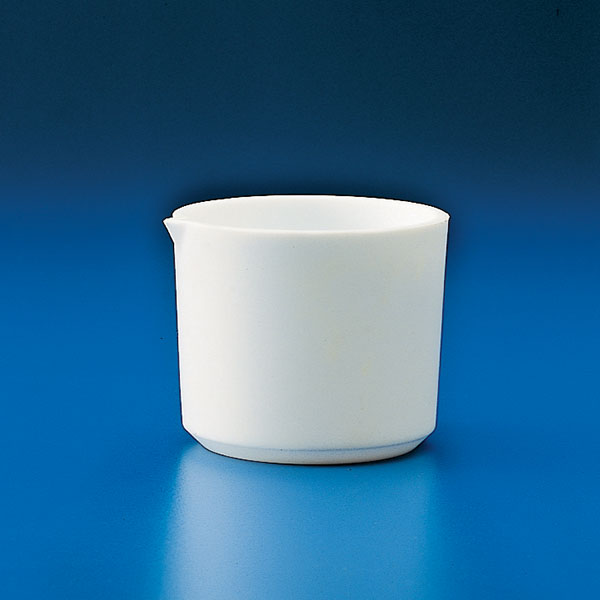
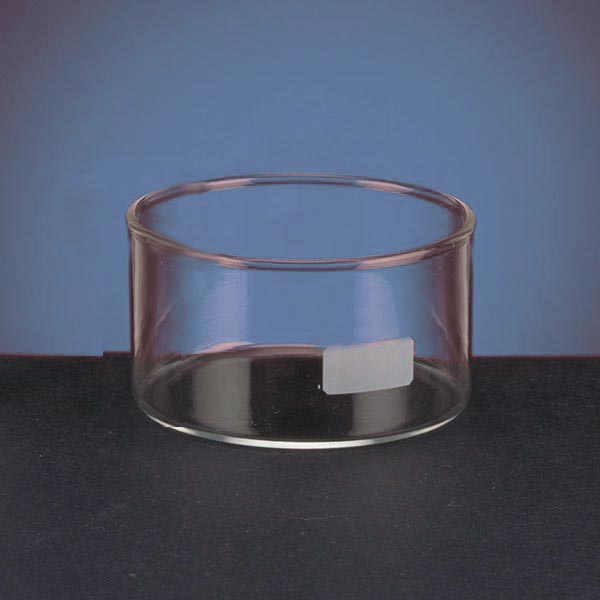
Capsules are generally made of porcelain, however, borosilicate glass and steel models can also be found. When used in contact with high temperatures, it is necessary that the capsule material is not damaged and does not contaminate its contents. For this reason, platinum models are also produced.
After they come into direct contact with a Bunsen burner, attention must be paid to their cooling. This must be done gradually, to prevent the capsule material from being damaged and cracks or breaks forming.
Shape and characteristics
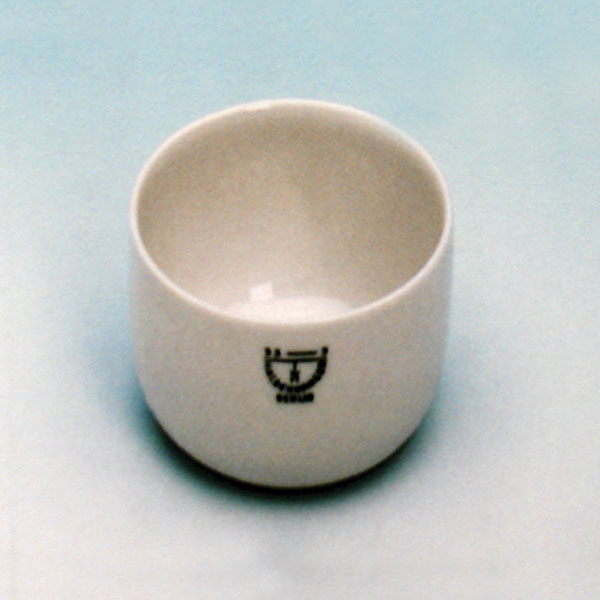
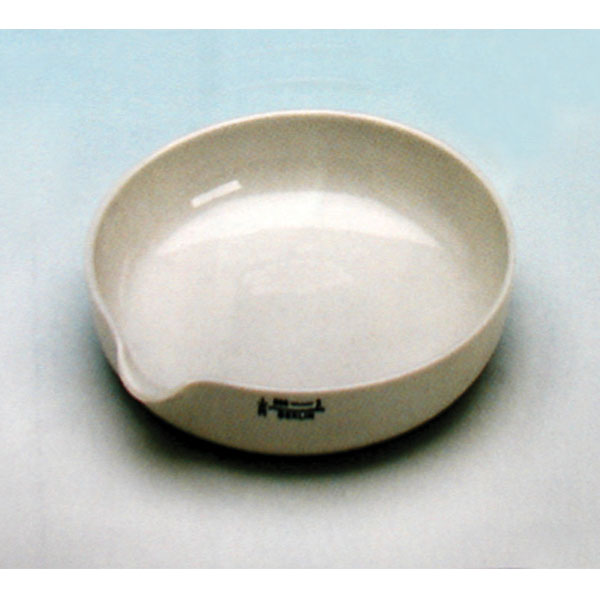
There are different capsule models, depending on their use. They are usually characterised by a cylindrical, low and flat shape. Their diameter is between 8 and 20 cm. while their capacity is between 3 ml and 10 ml.
The characteristic flat, cylindrical shape aids the evaporation process of the contents for two main reasons:
.
- The surface area of the liquid in contact with the air is greater than in a taller container.
The surface area of the liquid in contact with the air is greater than in a taller container.
- Unlike a dish, the walls of the capsule allow the vapour of the evaporated liquid condensed on its walls to escape into the container.
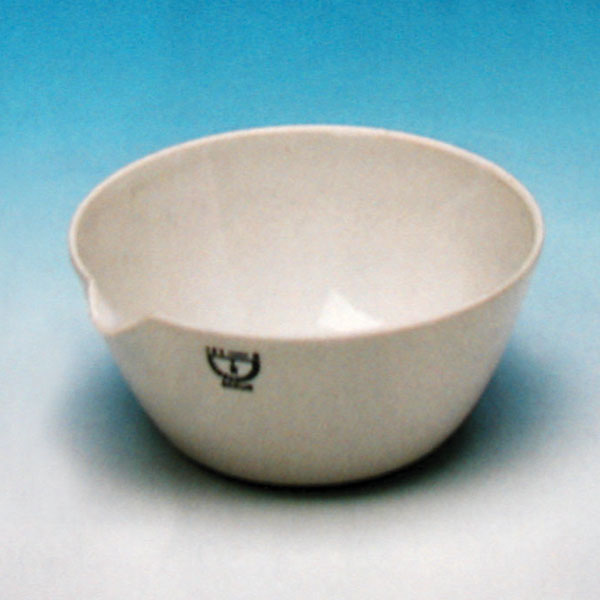
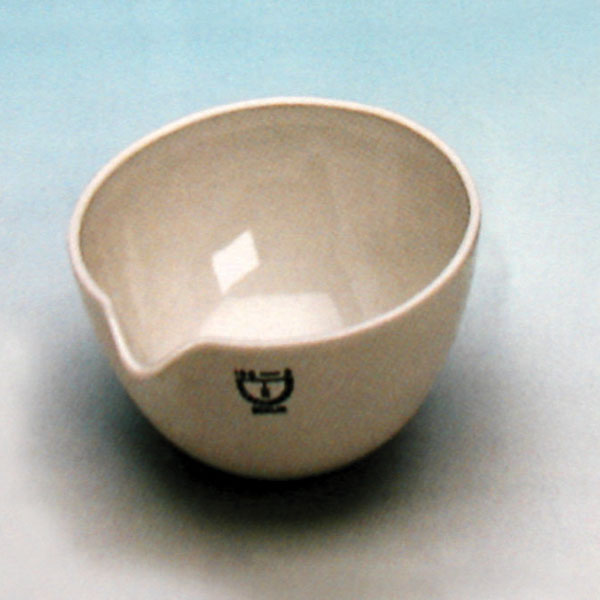
An additional feature of capsules is the pouring spout that can be found on the upper contour of the container. This is intended to help pour the contents more precisely. However, there are also alternative models that do not have a spout.
Main uses of capsules
.
One of the main uses of capsules is the evaporation of solutions. They are used to evaporate excess solvents, commonly water, to produce a more concentrated solution or the solid precipitate of the dissolved substance.
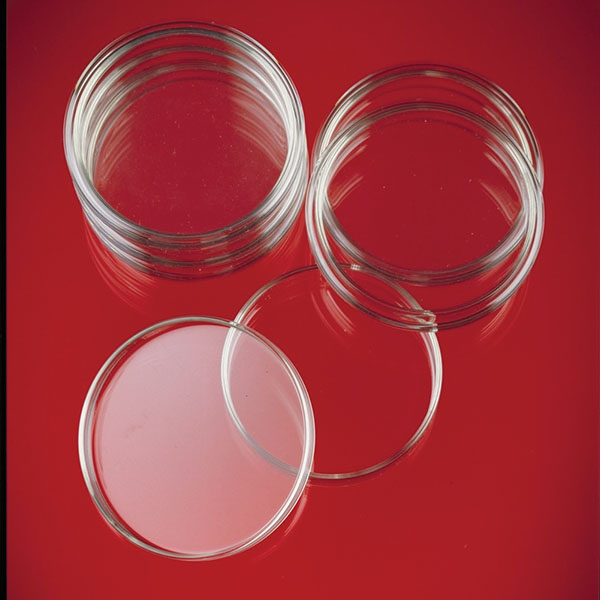
Petri dish
Also known as 'Petri dishes', they are a special capsule model characterised by a cylindrical shape and more sloping edges than a standard capsule model. This model is particularly used in biology as a container for culture media. It usually has a diameter of between 50 and 100 mm, and a height of about 15 mm.
Accessories
The most common accessory when working with a capsule is laboratory forceps. These are used to avoid direct contact with the capsule after it has been exposed to high temperatures. The tongs are generally made of steel.